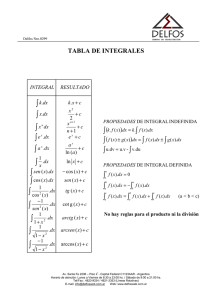
Apuntes - yoquieroaprobar.es
Anuncio
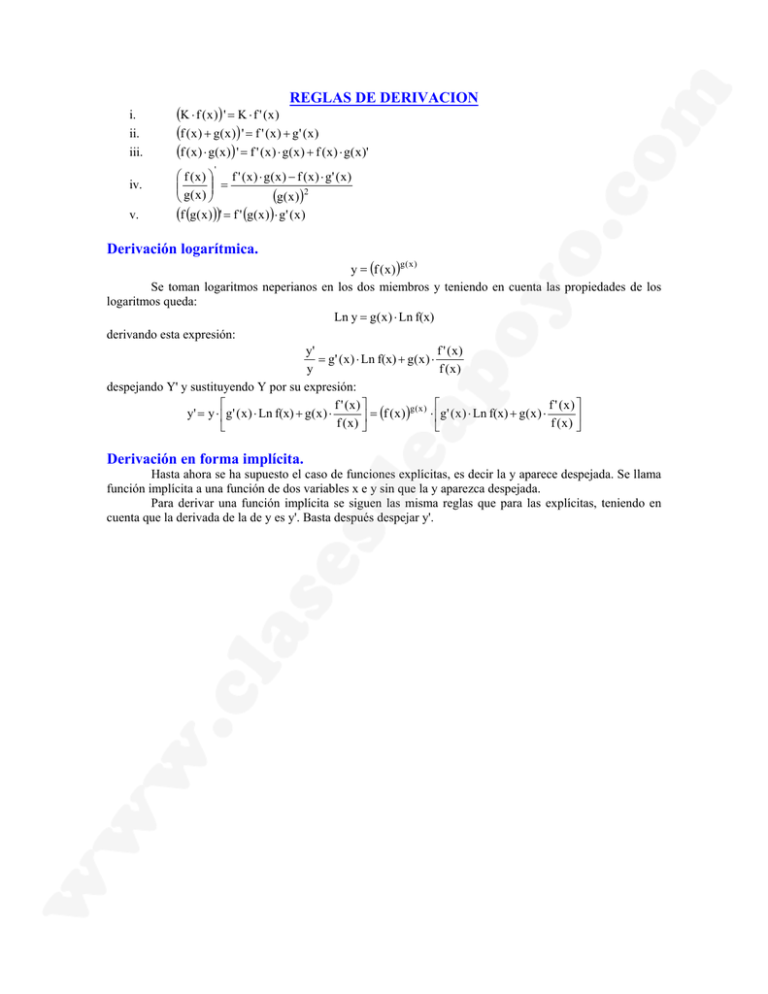
REGLAS DE DERIVACION i. ii. iii. (K ⋅ f ( x )) ' = K ⋅ f ' (x ) (f (x ) + g( x )) ' = f ' ( x ) + g' ( x ) (f (x ) ⋅ g( x ) ) ' = f ' (x ) ⋅ g( x ) + f (x ) ⋅ g(x )' ' iv. v. f (x ) f ' ( x ) ⋅ g(x ) − f (x ) ⋅ g' ( x ) = (g( x ) )2 g( x ) (f (g( x )))' = f ' (g(x ) )⋅ g' ( x ) Derivación logarítmica. y = (f ( x ) )g ( x ) Se toman logaritmos neperianos en los dos miembros y teniendo en cuenta las propiedades de los logaritmos queda: Ln y = g ( x ) ⋅ Ln f(x) derivando esta expresión: y' f ' (x) = g' ( x ) ⋅ Ln f(x) + g( x ) ⋅ y f (x) despejando Y' y sustituyendo Y por su expresión: f ' (x) f ' (x ) g(x) y' = y ⋅ g ' ( x ) ⋅ Ln f(x) + g ( x ) ⋅ ⋅ g' ( x ) ⋅ Ln f(x) + g ( x ) ⋅ = (f ( x ) ) f (x) f (x ) Derivación en forma implícita. Hasta ahora se ha supuesto el caso de funciones explícitas, es decir la y aparece despejada. Se llama función implícita a una función de dos variables x e y sin que la y aparezca despejada. Para derivar una función implícita se siguen las misma reglas que para las explícitas, teniendo en cuenta que la derivada de la de y es y'. Basta después despejar y'. Tabla de derivadas FUNCIÓN COMPUESTA REGLA DE LA CADENA y = f n (x) y' = n·f n−1 ( x )·f ' ( x ) y' = y = f (x ) y = f (x ) n FUNCION SIMPLE y' = 1 ·f ' ( x ) 2· f ( x ) 1 n·n (f ( x ) )n−1 ·f ' ( x ) y' = n·x n −1 y = xn y' = y= x y' = x 2· x 1 y' = n 1 n· x n −1 n y = a f (x) y' = a f ( x ) ⋅ f ' ( x ) ⋅ Ln(a ) y = ax y' = a x ⋅ Ln(a ) y = e f (x) y' = e f ( x ) ⋅ f ' ( x ) y = ex y' = e x y = Lg a (f ( x ) ) y' = 1 ·f ' ( x ) f ( x ) ⋅ Ln(a ) y = Lg a (x ) 1 ·f ' ( x ) f (x ) y = Ln(x ) y' = y = Ln(f ( x ) ) y' = 1 x ⋅ Ln(a ) y' = 1 x y = sen (f ( x ) ) y' = cos(f ( x ) ) ⋅ f ' ( x ) y = sen (x ) y' = cos(x ) y = cos(f ( x ) ) y' = −sen (f ( x ) ) ⋅ f ' ( x ) y = cos(x ) y' = −sen (x ) y' = y = tg (f ( x ) ) ( cos f ( x ) ⋅ f ' (x) = ) = 1 + tg 2 f ( x ) ⋅ f ' ( x ) y = arcsen(f ( x ) ) y' = y = ar cos(f ( x ) ) y' = y = arctg(f ( x ) ) 1 2 y' = 1 1 − f 2 (x) −1 1 − f 2 (x) 1 2 1 + f (x) y = tg (x ) y' = 1 2 cos x ⋅ f ' (x) y = arcsen(x ) y' = ⋅ f ' (x) y = ar cos(x ) y' = ⋅ f ' (x) y = arctg(x ) y' = = 1 + tg 2 x 1 1− x 2 −1 1− x 2 1 1+ x 2